Introduction
Ever found yourself wondering whether a colonoscopy could help detect prostate problems? You’re not alone. This article is here to guide you through these complex medical procedures, and understand their relevance to prostate health.
Understanding Colonoscopy
What is a Colonoscopy?
A colonoscopy is a medical procedure that allows doctors to examine the inner lining of your large intestine, specifically the colon and rectum. It helps to detect ulcers, colon polyps, tumors, and areas of inflammation or bleeding.
Why is a Colonoscopy Done?
A colonoscopy is typically performed to investigate intestinal signs and symptoms, screen for colorectal cancer, and look for more polyps if you’ve had them before.
Understanding Prostate Problems
What are Prostate Problems?
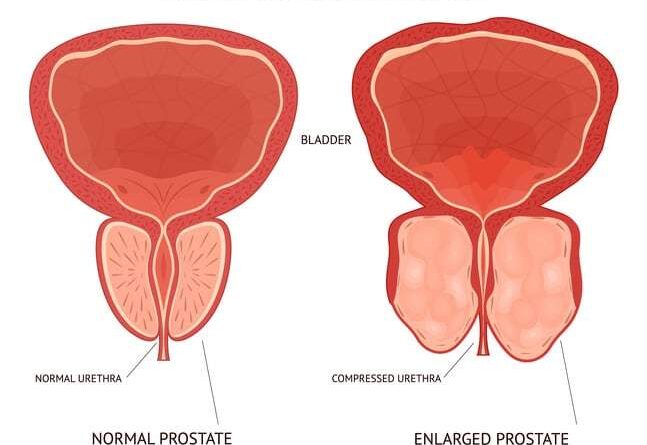
The prostate is a small gland in men that produces seminal fluid. Prostate problems commonly include benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), prostatitis, and prostate cancer.
Common Symptoms of Prostate Problems
These problems can present with various symptoms such as frequent urination, weak or interrupted urine flow, urinary retention, or pain during urination.
Can a Colonoscopy Detect Prostate Problems?
The Purpose of a Colonoscopy
A colonoscopy is used primarily to inspect the colon and rectum. So, is it useful in detecting prostate problems?
The Limitations of a Colonoscopy
In truth, a colonoscopy isn’t designed to identify prostate issues.
Why a Colonoscopy Might Not Detect Prostate Problems
Although the prostate is close to the rectum, it’s not part of the colon. Therefore, a colonoscopy isn’t able to diagnose prostate issues directly.
Alternative Methods for Detecting Prostate Problems
PSA Test
The Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) test is a blood test that can detect the early signs of an enlarged prostate and prostate cancer.
Digital Rectal Examination
A digital rectal examination is where a doctor or nurse uses their finger to feel for abnormalities in the prostate through the rectum.
In Conclusion
While a colonoscopy is a crucial tool for diagnosing issues related to the colon and rectum, it isn’t designed for detecting prostate problems. Understanding these limitations can help ensure that you’re using the right tools for your health needs and questions. As always, any health concerns should be discussed with a trusted healthcare provider. They can guide you in understanding the tests and procedures that are most beneficial to your health.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Why is a colonoscopy not suitable for detecting prostate problems? A colonoscopy is designed to examine the colon and rectum, not the prostate.
- What is the best method to detect prostate problems? The best method would depend on the individual’s symptoms, age, and overall health. However, the Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) test and Digital Rectal Examination (DRE) are commonly used for initial detection.
- Can colonoscopy detect any other health problems? Yes, a colonoscopy can detect a range of issues in the large intestine including ulcers, polyps, tumors, and inflammation or bleeding areas.
- Are there any side effects associated with colonoscopy? Side effects are relatively rare but may include mild cramping, bloating, or flatulence due to the air pumped into the colon during the procedure. In rare cases, complications such as colon perforation can occur.
- If not a colonoscopy, what routine check should men undergo for prostate health? Regular screenings such as PSA tests, especially for men over the age of 50, or for those with a family history of prostate problems, can be beneficial. However, it’s always best to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
- What age should men start checking for prostate problems? Screening for prostate problems typically begins at age 50 for most men, but it may start as early as 40 or 45 for men with a family history of prostate cancer or for African American men, who have a higher risk.
- Is colonoscopy a painful procedure? Most patients are sedated during a colonoscopy, which helps to minimize discomfort. Following the procedure, some people might experience minor bloating or gas pains.
- How frequently should a colonoscopy be done? If you’re at average risk of colon cancer, your doctor may recommend a colonoscopy every 10 years or sometimes sooner, starting at age 50. However, if you have higher risk factors, it may be recommended more frequently.
- What other tests are there for colorectal cancer? Apart from colonoscopy, other tests for colorectal cancer include fecal occult blood test (FOBT), sigmoidoscopy, and stool DNA test, among others.
- Can lifestyle changes reduce the risk of prostate problems? Yes, maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, eating a healthy diet, and avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol can help lower the risk of prostate problems.