Introduction
Hemorrhoids and prostate problems are two distinct conditions that can affect individuals, particularly as they age. Hemorrhoids refer to swollen veins in the rectal area, causing discomfort and pain, while prostate problems primarily involve the prostate gland, which is part of the male reproductive system. While these conditions may seem unrelated, there is a question worth exploring: Can hemorrhoids cause prostate problems? In this article, we will delve into both hemorrhoids and prostate problems, discussing their symptoms, risk factors, causes, diagnosis, treatment options, lifestyle changes, prevention methods, and potential complications. By the end, you will have a better understanding of whether hemorrhoids can indeed affect the prostate.
What are Hemorrhoids?
To comprehend the potential link between hemorrhoids and prostate problems, it is crucial to grasp what hemorrhoids are. Hemorrhoids, also known as piles, are swollen and inflamed veins in the rectal area or around the anus. They can develop internally or externally, leading to symptoms such as itching, discomfort, pain, and sometimes bleeding during bowel movements.
Understanding Prostate Problems
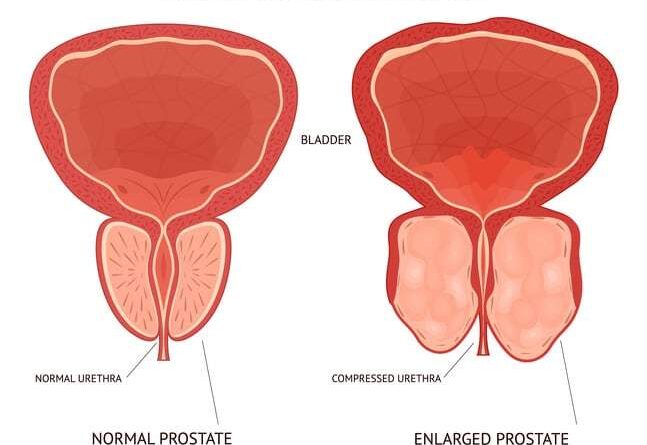
Before we investigate the correlation between hemorrhoids and prostate problems, let’s establish a foundation of knowledge about prostate problems themselves. The prostate gland is a vital component of the male reproductive system, located below the bladder and surrounding the urethra. It plays a role in the production of seminal fluid that nourishes and transports sperm. Common prostate problems include benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), prostatitis, and prostate cancer.
Can Hemorrhoids Affect the Prostate?
While hemorrhoids and prostate problems are distinct conditions, there is no direct evidence to suggest that hemorrhoids can cause prostate problems. The two conditions involve different anatomical structures and have separate underlying causes.
Common Symptoms of Hemorrhoids and Prostate Problems
Although hemorrhoids and prostate problems have different causes, they do share some similar symptoms. It’s important to recognize these symptoms to distinguish between the two conditions. Common symptoms of hemorrhoids include rectal itching, discomfort, pain, swelling, and bleeding during bowel movements. On the other hand, prostate problems can cause symptoms such as frequent urination, weak urine flow, difficulty starting or stopping urination, blood in the urine or semen, and pelvic pain. It is crucial to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis.
Risk Factors for Hemorrhoids and Prostate Problems
Certain risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing both hemorrhoids and prostate problems. While these risk factors do not directly establish a causal relationship between the two conditions, they contribute to their occurrence. Risk factors for hemorrhoids include straining during bowel movements, chronic constipation or diarrhea, obesity, pregnancy, a sedentary lifestyle, and a family history of hemorrhoids. On the other hand, risk factors for prostate problems include aging, family history of prostate issues, certain genetic factors, and hormonal imbalances.
Causes of Hemorrhoids and Prostate Problems
The causes of hemorrhoids and prostate problems differ significantly. Hemorrhoids are primarily caused by increased pressure on the veins in the rectal area. This can be due to straining during bowel movements, chronic constipation, pregnancy, or sitting for prolonged periods. Prostate problems, on the other hand, have various causes depending on the specific condition. Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is associated with hormonal changes and aging, while prostatitis can be caused by bacterial infections. Prostate cancer’s exact cause is still not fully understood but may involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Diagnosis of Hemorrhoids and Prostate Problems
To determine whether you have hemorrhoids or prostate problems, a healthcare professional will conduct a thorough evaluation. For hemorrhoids, a visual examination of the rectal area may be sufficient, but in some cases, additional tests like a digital rectal exam or anoscopy may be performed. Prostate problems, on the other hand, often require more comprehensive diagnostic procedures. These may include a digital rectal exam, prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood test, urine analysis, ultrasound, or a prostate biopsy to rule out prostate cancer.
Treatment Options for Hemorrhoids and Prostate Problems
The treatment approaches for hemorrhoids and prostate problems are distinct due to their different nature. Hemorrhoid treatment focuses on relieving symptoms and reducing inflammation. This may include lifestyle modifications such as increasing fiber intake, staying hydrated, and avoiding straining during bowel movements. Over-the-counter medications, topical creams, and warm baths may also provide relief. In more severe cases, procedures like rubber band ligation, sclerotherapy, or surgical removal may be necessary.
Prostate problems have a range of treatment options depending on the specific condition. Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) can be managed with medications that relax the prostate muscles or reduce hormone levels. If medications are ineffective, minimally invasive procedures like transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) or laser therapy may be recommended. Prostate cancer treatment can involve surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, hormone therapy, or a combination of these approaches.
Lifestyle Changes to Manage Hemorrhoids and Prostate Problems
In addition to medical treatments, making certain lifestyle changes can help manage hemorrhoids and prostate problems. For hemorrhoids, incorporating high-fiber foods into your diet, drinking plenty of water, and avoiding prolonged sitting can alleviate symptoms and prevent recurrences. Regular exercise and maintaining a healthy weight also play a significant role in managing hemorrhoids. For prostate problems, lifestyle changes may include adopting a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, and limiting alcohol and caffeine consumption. These lifestyle modifications can support overall prostate health and potentially alleviate symptoms associated with prostate problems.
Preventing Hemorrhoids and Prostate Problems
While it may not be possible to completely prevent hemorrhoids or prostate problems, certain measures can lower the risk of developing these conditions. For preventing hemorrhoids, maintaining regular bowel movements by eating a high-fiber diet, drinking plenty of fluids, and avoiding prolonged sitting or straining during bowel movements can be beneficial. Engaging in regular exercise and maintaining a healthy weight can also help reduce the risk of developing hemorrhoids.
Prevention strategies for prostate problems involve maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise. Additionally, routine check-ups with a healthcare professional can help identify any early signs or symptoms of prostate problems, allowing for timely intervention and management.
When to Seek Medical Help
If you experience persistent symptoms related to hemorrhoids or prostate problems, it is essential to seek medical help for proper evaluation and diagnosis. While hemorrhoids can often be managed with lifestyle changes and over-the-counter treatments, severe or recurring symptoms may require medical intervention. Similarly, if you notice symptoms such as urinary difficulties, persistent pelvic pain, blood in urine or semen, or other concerning signs related to the prostate, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional for a comprehensive assessment.
Complications of Hemorrhoids and Prostate Problems
Both hemorrhoids and prostate problems have potential complications that can arise if left untreated or unmanaged. Hemorrhoids may lead to complications such as thrombosis, where a blood clot forms within a hemorrhoid, causing severe pain. Prolonged or recurrent bleeding can also lead to anemia. In the case of prostate problems, complications can vary depending on the specific condition. For instance, untreated benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) can result in urinary tract infections, bladder stones, or kidney damage. Prostate cancer, if left untreated, can spread to other parts of the body, potentially causing life-threatening consequences.
In Conclusion
In conclusion, hemorrhoids and prostate problems are distinct conditions with separate causes and treatments. While there is no direct evidence suggesting that hemorrhoids can cause prostate problems, it is essential to understand the symptoms, risk factors, and management options for both conditions. Seeking medical help for proper diagnosis and treatment is crucial for individuals experiencing symptoms related to hemorrhoids or prostate problems. By adopting healthy lifestyle habits, following medical advice, and staying proactive about preventive measures, individuals can maintain good rectal and prostate health.
FAQs
1. Can hemorrhoids lead to prostate cancer?
No, there is no direct link between hemorrhoids and prostate cancer. Hemorrhoids are swollen veins in the rectal area, while prostate cancer is the abnormal growth of cells in the prostate gland. The two conditions have different causes and risk factors.
2. Can untreated hemorrhoids cause urinary problems?
Untreated hemorrhoids themselves do not typically cause urinary problems. However, if hemorrhoids are severe and cause significant discomfort or pain, they may indirectly affect urination patterns due to the discomfort associated with bowel movements.
3. Is surgery always required for treating hemorrhoids or prostate problems?
Surgery is not always necessary for treating hemorrhoids or prostate problems. In many cases, lifestyle changes, over-the-counter treatments, or medications can effectively manage the symptoms. However, in severe cases or when conservative measures fail, surgery may be considered as a treatment option.
4. Can hemorrhoids and prostate problems occur simultaneously?
Hemorrhoids and prostate problems can coexist in some individuals, but there is no direct causal relationship between the two conditions. They are separate entities that can occur independently. If you have concerns about both hemorrhoids and prostate problems, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate management.
5. Are there any natural remedies or home treatments for hemorrhoids and prostate problems?
While there are no guaranteed natural remedies for hemorrhoids or prostate problems, certain self-care measures may provide relief. For hemorrhoids, warm sitz baths, using witch hazel pads, applying ice packs, and using over-the-counter creams or ointments may help alleviate symptoms. However, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and guidance.
For prostate problems, lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy diet, regular exercise, and managing stress levels may contribute to overall prostate health. However, the specific treatment approach will depend on the underlying condition, and it is important to follow medical advice and treatment plans prescribed by healthcare professionals.
6. Can hemorrhoids or prostate problems be prevented entirely?
While it may not be possible to prevent hemorrhoids or prostate problems entirely, certain measures can reduce the risk of developing these conditions. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight, can contribute to overall rectal and prostate health. Additionally, practicing good bowel habits, such as avoiding straining during bowel movements and maintaining regular bowel movements, can help prevent hemorrhoids. Routine check-ups with healthcare professionals can aid in the early detection and management of prostate problems.
7. Can women develop prostate problems?
No, prostate problems are exclusive to individuals with a prostate gland, which is a part of the male reproductive system. Women do not possess a prostate gland, and therefore they do not develop prostate-related issues. However, women can experience other conditions related to the reproductive system, such as uterine fibroids or ovarian cysts, which may present with similar symptoms to prostate problems in males.
8. Can stress or anxiety contribute to the development of hemorrhoids or prostate problems?
Stress and anxiety are not direct causes of hemorrhoids or prostate problems. However, they can indirectly affect these conditions. Stress and anxiety may lead to changes in bowel habits, such as constipation or diarrhea, which can contribute to the development or worsening of hemorrhoids. Similarly, stress can potentially exacerbate symptoms of prostate problems, such as urinary difficulties. It is important to manage stress and seek appropriate stress-reduction techniques, along with following medical advice, for optimal rectal and prostate health.
9. Can a healthy diet prevent hemorrhoids or prostate problems?
Maintaining a healthy diet is beneficial for overall health, including rectal and prostate health. Consuming a diet rich in fiber, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can promote regular bowel movements, reduce the risk of constipation, and potentially decrease the likelihood of developing hemorrhoids. Similarly, a balanced diet that includes nutrient-dense foods and limits excessive fat intake may contribute to prostate health. While a healthy diet can support the prevention of these conditions, it is essential to combine it with other preventive measures and regular medical check-ups.
10. Can sexually transmitted infections (STIs) contribute to prostate problems?
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) can potentially lead to prostatitis, which is inflammation of the prostate gland. Certain bacterial infections, such as chlamydia or gonorrhea, can spread to the prostate and cause prostatitis. It is crucial to practice safe sex, use barrier methods like condoms, and seek timely medical treatment for STIs to minimize the risk of developing prostatitis or other complications related to the prostate.