Understanding Prostate Cancer and Catheterization
Introduction to Prostate Cancer
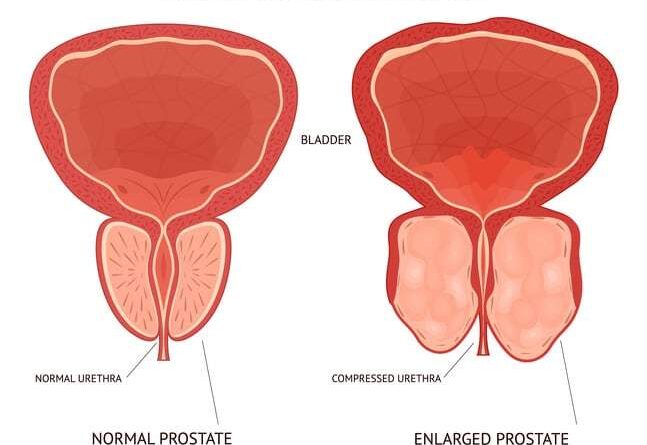
Prostate cancer, a common malignancy in men, begins in the prostate, a small gland that produces seminal fluid. It’s one of those diseases that can be silent, only making its presence known when it’s already advanced. The battle against prostate cancer often includes several treatment strategies, and occasionally, catheterization becomes a necessary part of the process.
What Is Catheterization?
Catheterization is a medical procedure that involves inserting a tube, known as a catheter, into the body. In the case of prostate cancer, a urinary catheter is typically used to help the patient urinate when they cannot do it independently.
Reasons for Catheterization in Prostate Cancer Patients
Catheterization in prostate cancer patients is often necessary after surgical procedures or when the cancer impedes normal urinary function. While it aids in essential bodily functions, it can also lead to some complications or discomforts, the focus of our discussion today.
Common Catheter Problems in Prostate Cancer Patients
Physical Discomfort and Pain
A significant concern with catheter use is the physical discomfort that comes with it.
Bladder Spasms
These can be characterized by a sudden, intense need to urinate and are caused by the bladder trying to expel the catheter.
Catheter Blockage
Blockages are another issue. If the catheter gets blocked, urine can’t be drained, leading to discomfort and potential complications.
Infections
A catheter, if not properly managed, can lead to urinary tract infections. These infections occur when bacteria climb up the catheter and into the bladder.
Urinary Problems
Catheter use can also result in urinary problems.
Leakage
Urine leakage, or bypassing, happens when urine leaks around the catheter rather than going through it.
Difficulty in Urinating
Some patients may have difficulty urinating after catheter removal, which can cause distress.
How to Manage Catheter Problems
There are solutions to address these issues.
Professional Medical Support
A healthcare professional’s guidance is essential in managing these complications. They can provide specific treatments and adjust the catheter as necessary.
Self-care Measures
Hygiene
Maintaining cleanliness around the catheter site is crucial to prevent infections.
Regular Catheter Change
Changing the catheter as advised by your healthcare provider can help prevent blockages and reduce the risk of infection.
In Conclusion
Facing prostate cancer is a journey, one that might include the use of a urinary catheter. While catheter-related problems such as discomfort, pain, infection, and urinary issues are common, they are manageable. By seeking professional medical support and practicing diligent self-care, these challenges can be overcome. Remember, it’s not just about the fight against cancer, but also about maintaining your quality of life throughout the journey.
FAQs
1. What can I do to prevent bladder spasms when using a catheter?
Bladder spasms can be controlled with certain medications. Also, maintaining a regular catheter cleaning schedule and avoiding irritants like caffeine and alcohol can help.
2. What are the symptoms of a urinary tract infection (UTI) due to catheter use?
Symptoms can include cloudy urine, a strong odor, fever, and pain in the lower abdomen or back. If you experience these symptoms, contact your healthcare provider immediately.
3. Why does urine leak around my catheter?
Urine leakage, or bypassing, can happen if the catheter becomes blocked or if bladder spasms occur. If leakage frequently happens, reach out to your healthcare provider.
4. How can I ensure proper hygiene with a catheter?
Cleaning the area around the catheter with mild soap and warm water at least once a day can help maintain hygiene. Also, remember to always wash your hands before and after handling your catheter.
5. Can I remove the catheter myself if I’m having difficulty urinating after its removal?
No, catheter removal should always be performed by a healthcare professional. If you’re having trouble urinating after catheter removal, contact your healthcare provider immediately.
6. What causes discomfort and pain when using a catheter?
Discomfort and pain are common when a catheter is first inserted. This typically decreases over time as individuals become accustomed to the catheter.
7. What types of catheters are used in prostate cancer patients?
The two main types of catheters used are indwelling catheters (also known as Foley catheters) and intermittent catheters. The choice depends on the patient’s specific needs and the duration for which the catheter is required.
8. What can cause a catheter blockage?
Blockages can occur due to the formation of blood clots or sediment in the urine. Prostate cancer itself may also increase the risk of blood clots, leading to potential blockages.
9. How are catheter blockages managed?
Regular flushing of the catheter can help prevent blockages. If a blockage does occur, the catheter may need to be removed or replaced by a healthcare professional.
10. What can be done to alleviate catheter-associated discomfort and pain?
Pain relief medication can help manage the discomfort and pain associated with catheter use. Over time, most patients also become more accustomed to the catheter, which can reduce discomfort.